The periodic table is an arrangment of the chemical elements ordered by atomic number so that periodic properties of the elements (chemical periodicity) are made clear.
Atomic Number 52
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-186450993-56a134a03df78cf77268608e.jpg)
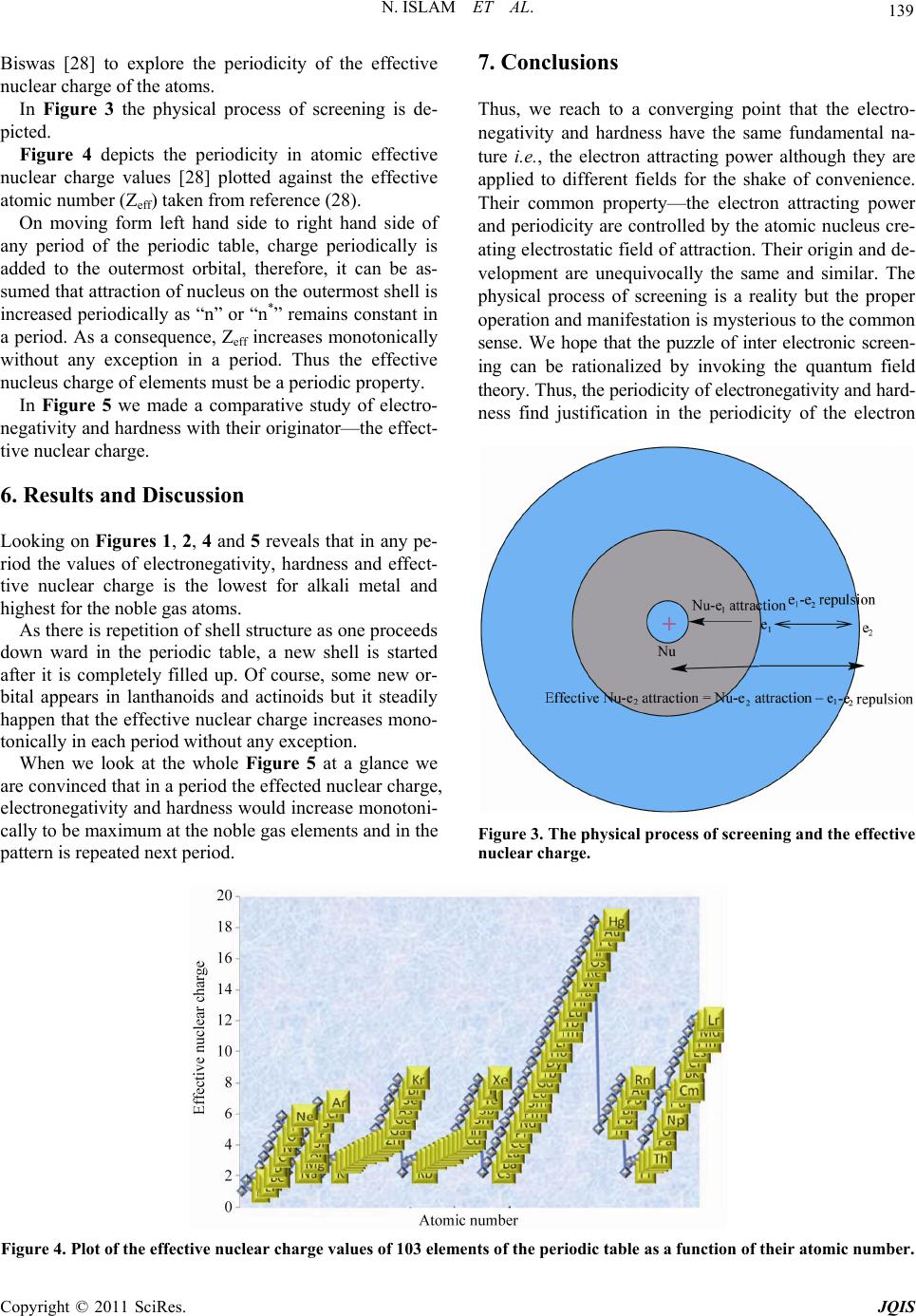
Explore the chemical elements through this periodic table
The number of atoms or molecules (n) in a mass (m) of a pure material having atomic or molecular weight (M) is easily computed from the following equation using Avogadro's number (NA = 6.022×10 23 atoms or molecules per gram-mole): M mN n A (1) In some situations, the atomic number density (N), which is the concentration of atoms or molecules per. Boron is the element that is atomic number 5 on the periodic table. It is a metalloid or semimetal that is a lustrous black solid at room temperature and pressure. Here are some interesting facts about boron. Fast Facts: Atomic Number 5.

| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period 1 | Hydrogen | Helium | |||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Lithium | Beryllium | Boron | Carbon | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Fluorine | Neon | |||||||||||
| 3 | Sodium | Magnesium | Aluminium | Silicon | Phosphorus | Sulfur | Chlorine | Argon | |||||||||||
| 4 | Potassium | Calcium | Scandium | Titanium | Vanadium | Chromium | Manganese | Iron | Cobalt | Nickel | Copper | Zinc | Gallium | Germanium | Arsenic | Selenium | Bromine | Krypton | |
| 5 | Rubidium | Strontium | Yttrium | Zirconium | Niobium | Molybdenum | Tc☢ Technetium | Ruthenium | Rhodium | Palladium | Silver | Cadmium | Indium | Tin | Antimony | Tellurium | Iodine | Xenon | |
| 6 | Caesium | Barium | * | Lutetium | Hafnium | Tantalum | Tungsten | Rhenium | Osmium | Iridium | Platinum | Gold | Mercury | Thallium | Lead | Bismuth | Po☢ Polonium | At☢ Astatine | Rn☢ Radon |
| 7 | Fr☢ Francium | Ra☢ Radium | ** | Lr☢ Lawrencium | Rf☢ Rutherfordium | Db☢ Dubnium | Sg☢ Seaborgium | Bh☢ Bohrium | Hs☢ Hassium | Mt☢ Meitnerium | Ds☢ Darmstadtium | Rg☢ Roentgenium | Cn☢ Copernicium | Nh☢ Nihonium | Fl☢ Flerovium | Mc☢ Moscovium | Lv☢ Livermorium | Ts☢ Tennessine | Og☢ Oganesson |
| *Lanthanoids | * | Lanthanum | Cerium | Praseodymium | Neodymium | Pm☢ Promethium | Samarium | Europium | Gadolinium | Terbium | Dysprosium | Holmium | Erbium | Thulium | Ytterbium | ||||
| **Actinoids | ** | Ac☢ Actinium | Th☢ Thorium | Pa☢ Protactinium | U☢ Uranium | Np☢ Neptunium | Pu☢ Plutonium | Am☢ Americium | Cm☢ Curium | Bk☢ Berkelium | Cf☢ Californium | Es☢ Einsteinium | Fm☢ Fermium | Md☢ Mendelevium | No☢ Nobelium | ||||
Atomic Number 56


The standard form of the periodic table shown here includes periods (shown horizontally) and groups (shown vertically). The properties of elements in groups are similar in some respects to each other.
There is no one single or best structure for the periodic table but by whatever consensus there is, the form used here is very useful and the most common. The periodic table is a masterpiece of organised chemical information and the evolution of chemistry's periodic table into the current form is an astonishing achievement.




